Climatology: Topic 13
Humidity & Dew Point : Understanding the Concept and Types
Humidity
- Humidity is a term used to describe the amount of water vapor present in the air.
- It is an important parameter as it has a significant impact on climate and weather patterns.
- In this article, we will discuss the concept of humidity, its types, and its relevance to UPSC exam.
Concept of Humidity
- Humidity is the amount of water vapor present in the air. It is often measured in terms of absolute humidity and relative humidity.
- Absolute humidity refers to the mass of water vapor per unit volume of air, while relative humidity is the ratio of the amount of water vapor in the air to the maximum amount that the air could hold at a given temperature.
Types of Humidity
There are several types of humidity, including absolute humidity, relative humidity, specific humidity, and dew point.
| Absolute Humidity | Relative Humidity | Specific Humidity | Dew Point |
| Actual amount of water vapor present in the air | Ratio of the amount of water vapor in the air to the maximum amount that the air could hold | Mass of water vapor per unit mass of air | Temperature at which the air would need to cool in order for water vapor to condense into water |
| Independent of air temperature & pressure | Dependent on air temperature and pressure | Independent of air temperature & pressure | Dependent on pressure: the higher the pressure, the lower the dew point temperature |
| Expressed in grams per cubic meter | Expressed as a percentage | Expressed in grams per kilogram | Dew point is given in °C Td |
Absolute Humidity
- Absolute humidity
- It is a measure of the amount of moisture present in the air, expressed as the mass of water vapor per unit volume of air.
- It is the actual amount of water vapor present in the air, expressed in grams per cubic meter.
- It indicates the total moisture content in the air and is independent of air pressure & temperature.
- Calculation
- Absolute humidity is calculated as the total mass of water vapor in a given volume of air, regardless of the air’s temperature or pressure.
- It is usually measured in grams per cubic meter (g/m3).
- Importance in weather forecasting, agriculture, and construction.
- In weather forecasting, absolute humidity is used to track the amount of moisture present in the atmosphere and to predict the likelihood of precipitation or other weather events. It is also an important factor in determining the heat index, which measures how hot the air feels to the human body based on the combination of temperature and humidity.
- In agriculture, absolute humidity is used to monitor the moisture content of crops and soil, which can affect crop growth and yield.
- In construction, absolute humidity is used to prevent moisture-related damage to building materials, such as mold growth or wood rot.
Relative Humidity
- Relative humidity is the ratio of the amount of water vapor in the air to the maximum amount that the air could hold at a given temperature.
- Calculation
- Relative humidity is expressed as a percentage and is calculated by dividing the amount of moisture present in the air by the maximum amount of moisture the air can hold at that temperature.
- Relative Humidity = [(Absolute humidity)/(Maximum water vapor air can hold at a given temperature)] X 100
- For example, if the air contains half of the moisture it can hold at a given temperature, the relative humidity is 50%. As the temperature increases, the air can hold more moisture, and thus the relative humidity decreases.
- Effects & Importance
- It affects the way we perceive temperature.
- When relative humidity is high, we tend to feel hotter than the actual temperature because our bodies have a harder time evaporating sweat.
- When relative humidity is low, we tend to feel cooler than the actual temperature because our bodies can evaporate sweat more easily.
- This is why relative humidity is often included in weather forecasts along with the actual temperature.
- Construction.
- High relative humidity can lead to mold and mildew growth, which can cause health problems and damage to buildings.
- Crops and Human Health
- Low relative humidity can cause dehydration, skin irritation, and other health problems, as well as damage to crops and soil.
- Water cycle and weather patterns
- When relative humidity is high, the air is more likely to form clouds and precipitation, leading to rainy weather.
- When relative humidity is low, the air is more likely to be dry, leading to clear skies and drier conditions.
- It affects the way we perceive temperature.
Specific Humidity
- Specific humidity is the mass of water vapor per unit mass of air.
- Calculation
- It is expressed in grams per kilogram and is a measure of the absolute amount of moisture in the air.
- Difference with Absolute and Relative Humidity
- Absolute humidity measures total amount of water vapor present in a given volume of air, but specific humidity measures the actual amount of water vapor in a unit of air mass.
- While relative humidity is useful in understanding the likelihood of precipitation or dew formation, specific humidity is more useful in understanding the actual amount of moisture present in the air.
- Importance
- Specific humidity is a critical factor in understanding the formation of clouds and precipitation. When specific humidity is high, it means that there is a large amount of moisture in the air, which can lead to the formation of clouds and eventually precipitation.
- Moreover, specific humidity is also important in understanding the impact of climate change on the environment. As global temperatures continue to rise, the atmosphere’s ability to hold moisture increases, leading to an increase in specific humidity. This, in turn, can lead to more extreme weather events such as heavy rainfall and flooding.
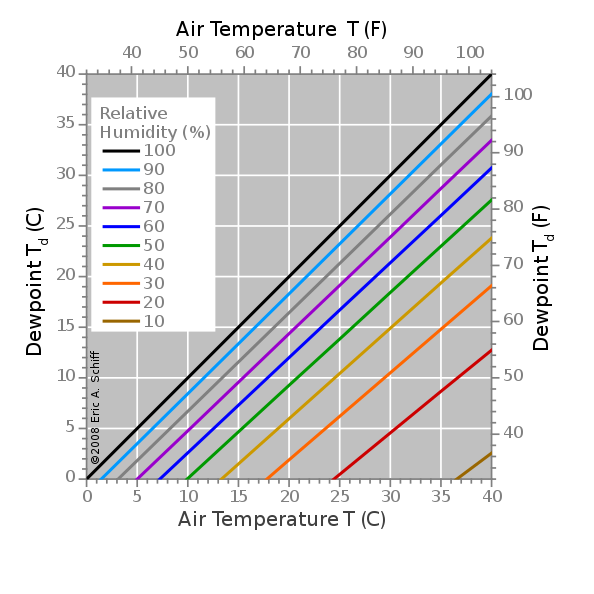
Dew Point
- What is Dew Point ?
- Dew point is a measure of the temperature at which moisture in the air condenses into liquid water. It is the climate point at which the relative air humidity equals 100% and begins to condense
- Dew point is the temperature at which the air needs to be cooled in order for water vapor to condense into liquid water.
- When air is cooled, its ability to hold moisture decreases. As the temperature drops, the air becomes saturated with water vapor and cannot hold any more. At this point, the water vapor begins to condense into liquid water, forming dew on surfaces such as grass, leaves, and car windshields. The temperature at which this occurs is known as the dew point.
- Calculation
- Devices called hygrometers are used to measure dew point over a wide range of temperatures
- Mathematical calculation is not important for UPSC exam, however a simpler formula to calculate dew Point is given below
- The dew point is given in °C Td
- Td = T – ((100 – RH)/5), where Td is dew point temperature (in degrees Celsius), T is observed temperature (in degrees Celsius), and RH is relative humidity (in percent).
- Factors affecting Due Point
- The dew point is influenced by factors such as air temperature, humidity, and pressure.
- Higher levels of humidity lead to a higher dew point, as there is more moisture in the air that can condense into liquid water.
- Conversely, lower levels of humidity result in a lower dew point.
- Is Dew point a type/measure of humidity ?
- While it is not a measure of the amount of water vapor present in the air like absolute humidity, relative humidity, and specific humidity, it is a measure of the point at which water vapor in the air will condense into liquid water.
- When the air temperature cools to the dew point, the air becomes saturated with moisture and water droplets begin to form on surfaces.
- So, the dew point is an important indicator of the likelihood of dew, fog, or frost formation, which is related to the amount of moisture present in the air.
- Therefore, while dew point is not a direct measure of humidity, it is a useful measure for understanding the moisture content of the air and its potential impact on the environment.
- Importance
- Helps predict weather patterns
- As air temperature drops, it reaches a point where it can no longer hold all the moisture present in the atmosphere, and excess moisture condenses into liquid water, forming dew. This process can also lead to fog formation.
- By monitoring dew point, meteorologists can predict the likelihood of dew, fog, or frost formation, which is essential for weather forecasting.
- Agriculture
- Soil moisture and crop growth are directly related, and dew formation can play a critical role in providing moisture to crops during dry spells.
- Additionally, monitoring dew point can help farmers make informed decisions about irrigation and crop management.
- Construction
- Dew point is an important factor in preventing condensation on building materials.
- When moist air comes into contact with a surface that is at or below the dew point, condensation occurs, leading to damage to the building material.
- By monitoring dew point, builders can take preventive measures to prevent condensation from forming on building materials, such as insulation, to avoid damage and prolong their lifespan.
- Helps predict weather patterns
Humidity in India
- India is a country with diverse climatic conditions, and the level of humidity varies greatly across its different regions.
- Coastal regions such as Kerala, Goa, and Mumbai experience high levels of humidity due to their proximity to the sea.
- The northeastern region of India experiences high levels of humidity during the monsoon season, while the arid regions of Rajasthan and Gujarat have low humidity levels.
- Relative humidity is an important factor in determining the level of comfort in a particular region. High levels of humidity can make the air feel warmer than it actually is, while low humidity levels can lead to dry skin and respiratory problems.
Relevance to UPSC Exams
The study of humidity is an important topic in geography, and it is relevant to both the Prelims and Mains exams of the UPSC civil services. Candidates should have a good understanding of the different types of humidity, their measurement, and their impact on climate and weather patterns. They should also be familiar with the humidity levels in different regions of India and the factors that contribute to these levels.
Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
1. Which of the following measures the actual amount of water vapor present in the air?
a) Relative humidity
b) Specific humidity
c) Absolute humidity
d) Dew point
Answer: c)
2. At what relative humidity does the air become saturated?
a) 100%
b) 50%
c) 75%
d) 25%
Answer: a)
3. Which of the following is a measure of the mass of water vapor per unit mass of air?
a) Absolute humidity
b) Relative humidity
c) Specific humidity
d) Dew point
Answer: c)
4. What is the dew point temperature when the air is fully saturated?
a) Higher than the air temperature
b) Equal to the air temperature
c) Lower than the air temperature
d) None of the above
Answer: b)
5. Which of the following is NOT a factor affecting humidity?
a) Air temperature
b) Air pressure
c) Wind speed
d) Atmospheric gases
Answer: d)
6. What is the term used to describe the ratio of the actual vapor pressure to the saturated vapor pressure at a given temperature?
a) Absolute humidity
b) Relative humidity
c) Specific humidity
d) Dew point
Answer: b)
7. Assertion: Humidity affects the rate at which sweat evaporates from the skin.
Reason: Higher humidity reduces the rate of sweat evaporation.
a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is NOT the correct explanation of the assertion.
c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer: a)
8. Which of the following is the temperature at which the air would need to be cooled in order for water vapor to condense into liquid water?
a) Absolute humidity
b) Relative humidity
c) Specific humidity
d) Dew point
Answer: d)
9. Which of the following is true regarding the relationship between temperature and humidity?
a) Higher temperatures lead to lower humidity.
b) Lower temperatures lead to lower humidity.
c) Higher temperatures lead to higher humidity.
d) There is no relationship between temperature and humidity.
Answer: c)
10. Which of the following is NOT a type of humidity?
a) Absolute humidity
b) Dry humidity
c) Specific humidity
d) Relative humidity
Answer: b)
11. Which of the following factors influence the dew point?
a) Air temperature and pressure
b) Wind speed and humidity
c) Relative humidity and atmospheric gases
d) Air temperature and humidity
Answer: d)
12. Which of the following is a useful measure of the moisture content in the air in industries such as food processing?
a) Absolute humidity
b) Relative humidity
c) Specific humidity
d) Dew point
Answer: a)
13. Assertion: Higher humidity makes the air feel warmer than it actually is.
Reason: Higher humidity reduces the rate of sweat evaporation, which makes the body feel warmer.
a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is NOT the correct explanation of the assertion.
c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer: a)